Everyone Said Toyota Was Late To EVs, Now It’s About To Lead Them

- Toyota plans to launch the world’s first all-solid-state battery EV by 2027.
- New batteries promise faster charging, longer range, and greater durability.
- Other carmakers, like BMW and Honda, are also developing solid-state cells.
Toyota has come under plenty of criticism in recent years for not making the shift to electric powertrains as quickly as some of its competitors. However, the world’s largest car manufacturer continues to invest heavily in EV technologies, doubling down on its commitment to launch new models with all-solid-state batteries in 2027-2028.
Since 2021, Toyota has been working with Japanese mining company Sumitomo Metal Mining on the cathode materials needed for solid-state batteries. These batteries, primarily composed of a cathode, anode, and solid electrolyte, have long been considered the holy grail of electric vehicles.
Smaller, Lighter, Faster
Beyond improving range, solid-state batteries are expected to be smaller, lighter, and charge faster than today’s lithium-ion packs. The technology is also said to deliver higher output and longer life.
Toyota recently signed a new agreement with Sumitomo Metal Mining to accelerate the mass production of these cathode materials, taking another step toward commercializing the technology.
Read: Toyota Partners With Japanese Petroleum Giant To Develop Solid-State Batteries For EVs
Toyota and Sumitomo say that through the use of powder synthesis technology, they have been able to develop a “highly durable cathode material” that can be mass-produced for these batteries. The collaboration builds on Sumitomo’s experience supplying cathode materials for existing EVs, now adapted to the stricter requirements of solid-state production.
It’s not just its work with Sumitomo that will allow Toyota to commercialize solid-state batteries. Since 2013, it has also been working alongside Japanese oil product Idemitsu Kosan on the new technology.
Idemitsu Kosan is developing lithium sulfide for use in batteries and plans to build a large plant capable of producing 1,000 metric tons of the material annually. Mass production is expected to start in 2027.

A previous roadmap published by Toyota indicated that its first generation of solid-state batteries launching in 2027-2028 will allow for 1,000 km (621 miles) worth of range, all while having the ability to charge from 10-80 percent in just 10 minutes.
The second generation is projected to exceed 1,200 kilometers (745 miles), signaling a substantial leap in energy density and efficiency.
In a statement, Toyota and Sumitomo said they are currently focusing on improving the “performance, quality, and safety of cathode materials for all-solid-state batteries, as well as reducing costs for mass production.” They aim to “achieve the world’s first practical use of all-solid state batteries in BEVs.”
Global Race For Solid-State Supremacy
While Toyota hopes to lead the transition, several global automakers are pursuing the same goal. BMW, Honda, Stellantis and Mercedes are investing heavily in solid-state technology, with some already testing prototype vehicles. Recently, MG launched the second-generation MG4 with semi-solid-state batteries that use around five percent liquid electrolyte.
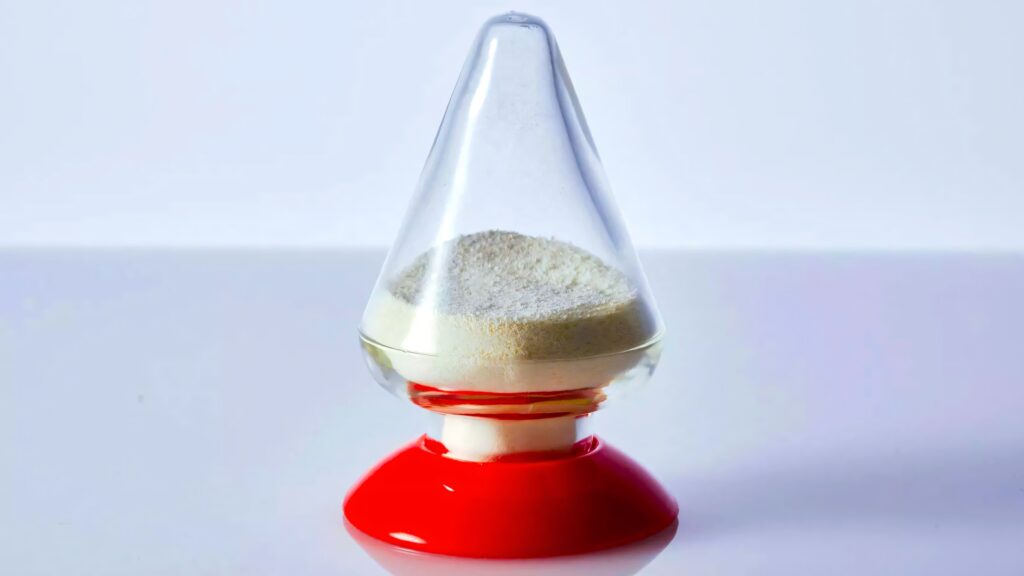
Note: For anyone wondering, the opening image shows a pear-shaped lab flask containing a sample of solid-state battery material. Toyota included the photo in a release about its all-solid-state battery program.
Despite online jokes about the shape, it’s actually a standard scientific container used for drying and storing chemical samples during testing and production. The powder inside is cathode or electrolyte material destined for Toyota’s next-generation solid-state EV batteries.
































 A German startup believes it has the recipe for electric vehicle battery cells that are cheaper, more energy dense, and less problematic for the environment than current lithium-ion cells. But commercialization seems a long way off. Theion announced Thursday in a press release that it is close to completing a 15 million euro (approximately $16.2...
A German startup believes it has the recipe for electric vehicle battery cells that are cheaper, more energy dense, and less problematic for the environment than current lithium-ion cells. But commercialization seems a long way off. Theion announced Thursday in a press release that it is close to completing a 15 million euro (approximately $16.2...  Chinese researchers claim to have developed a process to recover nearly all of the lithium from used electric vehicle batteries for recycling. The Independent (via InsideEVs) reports on study results first published in the German academic journal Angewandte Chemie claiming recovery of 99.99% of lithium from a used battery, as well as 97% of nickel...
Chinese researchers claim to have developed a process to recover nearly all of the lithium from used electric vehicle batteries for recycling. The Independent (via InsideEVs) reports on study results first published in the German academic journal Angewandte Chemie claiming recovery of 99.99% of lithium from a used battery, as well as 97% of nickel...  Deployment of 5-minute battery swaps could support hundreds of commercial EVs Ample says it's a straightforward retrofit, switching to its own battery packs Solution is less demanding on the grid than fast-charging stations California-based startup Ample is looking to deploy its battery-swapping tech with fleets of electric delivery trucks in...
Deployment of 5-minute battery swaps could support hundreds of commercial EVs Ample says it's a straightforward retrofit, switching to its own battery packs Solution is less demanding on the grid than fast-charging stations California-based startup Ample is looking to deploy its battery-swapping tech with fleets of electric delivery trucks in...  Chinese battery firm CATL and automaker Nio are preparing to launch what the two companies claim will be the world's largest electric vehicle battery swapping network. CATL and Nio announced a technical partnership last year that included battery swapping, but on Tuesday they confirmed plans to start coordinating efforts as they build out battery...
Chinese battery firm CATL and automaker Nio are preparing to launch what the two companies claim will be the world's largest electric vehicle battery swapping network. CATL and Nio announced a technical partnership last year that included battery swapping, but on Tuesday they confirmed plans to start coordinating efforts as they build out battery...